The Crisis Report - 91
Short Take #03 - Do you want to see what a SUCCESSFUL Carbon Storage and Sequestration (CSS) solution looks like?

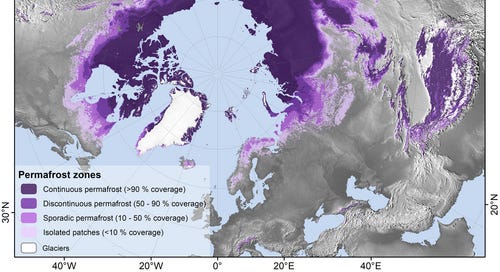
PERMAFROST is what REAL CSS done on a planetary scale looks like.

If “PERMAFROST” was a CSS company it was only founded about 750,000 years ago. Before then, there was NO Permafrost. There was no Ice Cap on Greenland. Arctic sea ice was probably a “year round” thing but it hadn't been for long.
At +2.0°C we think that the Arctic Ice Cap will completely melt during the Summer months.

Arctic summer sea ice could disappear as early as 2035 — (pub. 2020)
FYI — We are also now “on track” to reach +2.0°C of WARMING by 2035.
This is a Warming FEEDBACK.
Sea ice covered with fresh snow reflects roughly 85% of the sunlight that falls on it, whereas open Arctic waters reflect only about 7%.
When the Arctic Ocean becomes ice free during the summer in a few decades, it will absorb about +78% more energy. Arctic warming will accelerate rapidly as this happens. Models suggest this will add +0.5℃ to global warming in addition to the warming caused by CO2 and CH4.
Arctic warming will accelerate rapidly as the Summer Sea Ice shrinks. Models suggest this will add +0.5℃ to overall global warming.
This reality makes it “highly likely” that the Rate of Warming will accelerate as the Arctic Sea Ice shrinks over the next ten years.
There is NO Permafrost older than 700,000 years. What does that tell us?
It tells us that the “Arctic as we know it” is a FRAGILE ARTIFACT of an Extreme Ice House Climate.

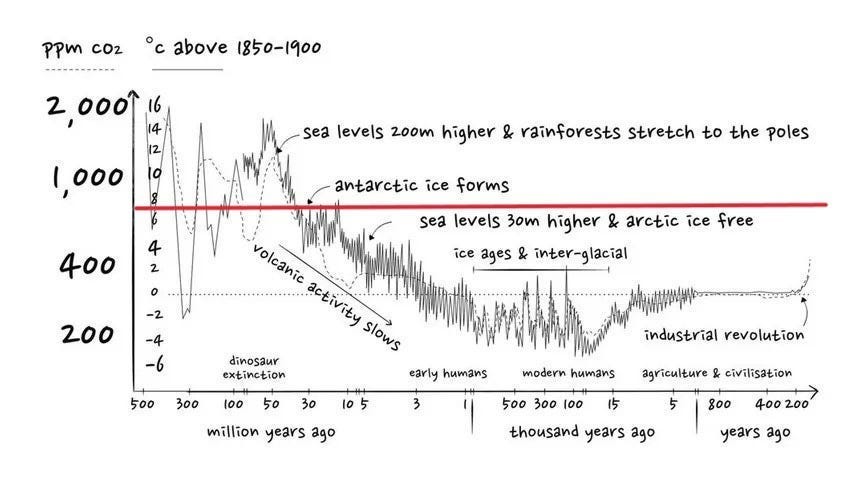
The permafrost acted as an efficient, if slow, CSS system. Over roughly 50,000 years it pulled enough CO2 out of the atmosphere that the atmospheric CO2 dropped to a low of just 180ppm.
Temperatures fell -6.0°C and glaciers covered the Northern Hemisphere.
The last 800,000 years the Earth has been in an Extreme Ice House climate state. The Boreal Zone (permafrost and forest) carbon sink relentlessly pulls CO2 out of the atmosphere and sequesters it.
The Permafrost and Boreal Forests of the High Arctic have been the planetary CSS system for the last 800,000 years. They have prevented the atmospheric CO2 level from getting above 300ppm during this period.
There is a LOT of organic carbon stored in the Boreal Forests and permafrost.
THERE IS ENOUGH ORGANIC CARBON IN THE PERMAFROST TO INCREASE THE ATMOSPHERIC CO2 LEVEL TO ABOUT 1300PPM.
We “underestimated” how big the permafrost actually was from the start of Climate Science. Not by a little, by a LOT.
It wasn’t until the 00’s that we did an actual “on the ground” comprehensive survey of how much permafrost actually exists. It found 2X more than had been estimated. Which would be of minor interest if that estimate hadn’t been part of our Climate Models since the 70's.
In 2008, the first REAL study of Arctic permafrost and its potential to influence the Climate System, DOUBLED the estimate for the amount of organic carbon held in permafrost soils.
Vulnerability of Permafrost Carbon to Climate Change: Implications for the Global Carbon Cycle.
How do you think the Climate Moderates dealt with this finding?
As you might expect, they decided that the permafrost would melt SLOWLY and they THEORIZED that the organic carbon in the permafrost would be released SLOWLY via biological processes.
Iron mineral dissolution releases iron and associated organic carbon during permafrost thaw
Nature Communications volume 11, Article number: 6329 (2020)
There may be greater CO2 emissions associated with thawing Arctic permafrost than ever imagined. An international team of researchers, including one from the University of Copenhagen, has discovered that soil bacteria release CO2 previously thought to be trapped by iron. The finding presents a large new carbon footprint that is unaccounted for in current climate models.
Arctic permafrost releases more CO2 than once believed (2021)
As it actually turns out that, iron doesn’t necessarily bind organic carbon after all.
Researchers have long been aware that microorganisms play a key role in the release of CO2 as permafrost melts. Microorganisms activated as the permafrost thaws convert dead plants and other organic material into greenhouse gases like methane, nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide.
It was believed that the mineral iron would bind carbon even as permafrost thawed. The new field study demonstrates that bacteria incapacitate iron’s carbon trapping ability, resulting in the release of vast amounts of CO2. This is an entirely new discovery.
“What we see is that bacteria simply use iron minerals as a food source. As they feed, the bonds which had trapped carbon are destroyed and it is released into the atmosphere as greenhouse gas,” explains Associate Professor Carsten W. Müller of the University of Copenhagen’s Department of Geosciences and Natural Resource Management. He elaborates:
“Frozen soil has a high oxygen content, which keeps iron minerals stable and allows carbon to bind to them. But as soon as the ice melts and turns to water, oxygen levels drop and the iron becomes unstable. At the same time, the melted ice permits access to bacteria. As a whole, this is what releases stored carbon as CO2.”
The amount of stored carbon that is bound to iron and will get converted to CO2 when released, is estimated to be somewhere between two and five times the amount of carbon released annually through anthropogenic fossil fuel emissions.
If just 50% of the carbon frozen in the permafrost becomes CO2, that will add about 280ppm to the atmospheric CO2 level. If we put ZERO CO2 into the atmosphere from this point forward, atmospheric CO2 levels could still climb to +700ppm.
Which would probably melt half of Antarctica and raise the Global Mean Temperature by at least +7°C.
The Moderates who have dominated Climate Science since the 70’s, MINIMIZED these risks in their models because that’s the only way to make REALITY fit their theories.
Our models are WRONG.
Terrifying Study Finds Melting Permafrost Could Unleash Way More Carbon Than We Thought. (2021)
While the Arctic was previously considered a carbon sink, new research shows that the region is emitting more carbon than it is absorbing, largely due to permafrost thaw. It is estimated that the world’s permafrost contains up to 1,700 billion tonnes of carbon, which is almost double the amount of carbon in the Earth’s atmosphere, and four times more than what has already been emitted by humans as since the Industrial Revolution.
If all permafrost were degraded to the point of decomposing, the disastrous effects would be felt all over the world.
Arctic permafrost is now a net source of major greenhouse gases — New Scientist 12 April 2024.
An Arctic-wide survey has found that the permafrost region is emitting more carbon into the atmosphere than it absorbs, causing the planet to heat even further.
THERE IS ENOUGH ORGANIC CARBON IN THE PERMAFROST TO INCREASE THE ATMOSPHERIC CO2 LEVEL TO ABOUT 1300PPM.
Half of this frozen organic matter is found in the first 3 meters of the permafrost.
It’s melting. WAY faster than the models indicated it would.
“Observed maximum thaw depths at our sites are already exceeding those projected to occur by 2090 under representative concentration pathway version 4.5.”
In 2020 the Arctic Institute warned that a 3 degree Celsius increase in global temperatures could melt 30 to 85 percent of the top permafrost layers that exist across the Arctic region.
The Arctic has warmed nearly four times faster than the globe since 1979
Communications Earth & Environment volume 3, Article number: 168 (Aug 2022)
700,000 years of Organic Carbon have ACCUMULATED in the Permafrost Zone.
In fact, the “Boreal Zone” has functioned as a carbon sink for so long that if you burned all of the oil available in all the reserves around the world, you would still release less carbon than the boreal forest and permafrost is currently holding.
Until recently NO ONE was checking to see if reality was conforming to the Climate Models.
The attitude has been something like this statement from climate researcher Dr. Andrew Dessler in an NYT interview in Dec. 2023 about the “unprecedented” warming in 2023.
“Your default position has to be, ‘The models are right.”
They were WRONG about EVERYTHING. Particularly about how FAST the permafrost could release carbon. Everyone thought melting permafrost would be waterlogged and swampy.
WHO KNEW IT WOULD DRY OUT AND BURN?
Climate Change Is So Bad, Even the Arctic Is On Fire.
bloomberg.com September 23, 2024
From Siberia to Brazil, wildfires are moving underground and burning up massive carbon deposits. The resulting emissions threaten to worsen global warming.
What sets these fires apart is their tendency to move below ground into carbon-rich soil layers.
While wildfires generally flame upwards quickly consuming forest and grassland the increasingly intense blazes of recent years move downward, where they smolder flamelessly below the surface, consuming layers of organic material.
These little-studied fires are becoming more common as severe wildfires have doubled in frequency over the past two decades.
In the Arctic, 2024 is shaping up to be the worst fire year since 2020, when blazes burning across Siberia for several months consumed 8.6 million acres of tundra and sent emissions surging to a record.
This is ALSO a Warming FEEDBACK.
It’s pretty clear. It’s going to get a LOT HOTTER a LOT FASTER than the Moderates thought.
The CONSEQUENCES of Permafrost Melt are going to be SEVERE.
rc 092624
Personal Notes:
I have been looking at feedbacks a lot right now so this report in Bloomberg triggered this response. I am not surprised by this news, but I hadn’t thought of it. I have also been guilty of thinking of melting permafrost as being wet. The word “melting” shapes your perception and blinds you to seeing all the possibilities.
As a feedback, this is BAD news.
There is a LOT of carbon locked up in the permafrost. About 800,000 years worth of organic debris is in those deposits.
It has been assumed that IF the permafrost melted (FYI — the Moderates have minimal permafrost melt in their models) that much of that carbon would be “locked up”. That biological processing of it would be slow and happen over a long period.
This suggests a RAPID release of carbon from the permafrost burning is not only possible but the “most likely” outcome.
In Hansen’s”Global Warming in the Pipeline” paper he forecasts a +8°C to +12°C rise in the GMT. In large part from the permafrost melting and releasing carbon and methane. He sees it as a SLOW process over hundreds of years.




Thank you for that information. It is as I expected, but had never put numbers to.
Your comment about underground fires reminded me of coal tip fires from my youth in a coal mining area. They would burn for years, often almost invisible unless it rained and the steam could be seen rising. They were impossible to put out.
As I recall, damp coal could self ignite. It could happen in steam ship coal stores, if the coal was loaded wet. Presumably something similar may happen in thawing peat beds.
Have you come across any information or assessments of methane clathrates and their current status underwater? As ocean waters are heating up faster than expected, one might expect that sedimentary coastal shelves may release increasing methane underwater. As I understand it, the quantities are massive, and could further accelerate warming very quickly.
Thanks for that, Richard! However, you focused on the carbon burning and CO2 release issue, and I'm looking at the 144 BTUs of heat energy absorbed by one pound of melting ice, when the net tells me that 6mm of the top layer of permafrost are melting annually and 22% of the land area in the northern hemisphere is covered with permafrost. So that's roughly 140 X 10 to the 6th times 22% or about 30,000,000 sq. mi. of permafrost, with 6mm of ice melting annually. This enormous amount of heat energy absorption is never mentioned and it is the "canary in the coal mine" for global heat imbalance calculations. I'll let the next guy/gal work out the BTUs being absorbed, but I'm guessin' it approaches the amount of heat energy being absorbed by the 321 X 10 to the 6th cubic miles of oceans and just as important, especially when it's gone.