The Crisis Report - 39
Anthropogenic Particulate is a form of Geoengineering. Dissecting a Climate Disinformation Campaign and Discussing Historical Geoengineering of the Climate. - Final
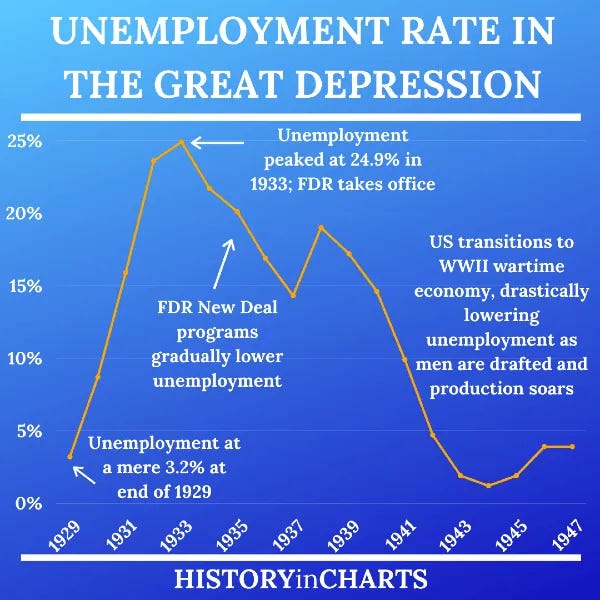
Let's talk about what happened to the Climate System in the 30’s.

In the 30’s the global economy crashed (The Great Depression), this resulted in a lot less particulate pollution.

It wasn't an “accident”. It was bad government and lack of regulation on the financial system.

This “social disaster” had a BIG effect on the Earth’s Climate System.
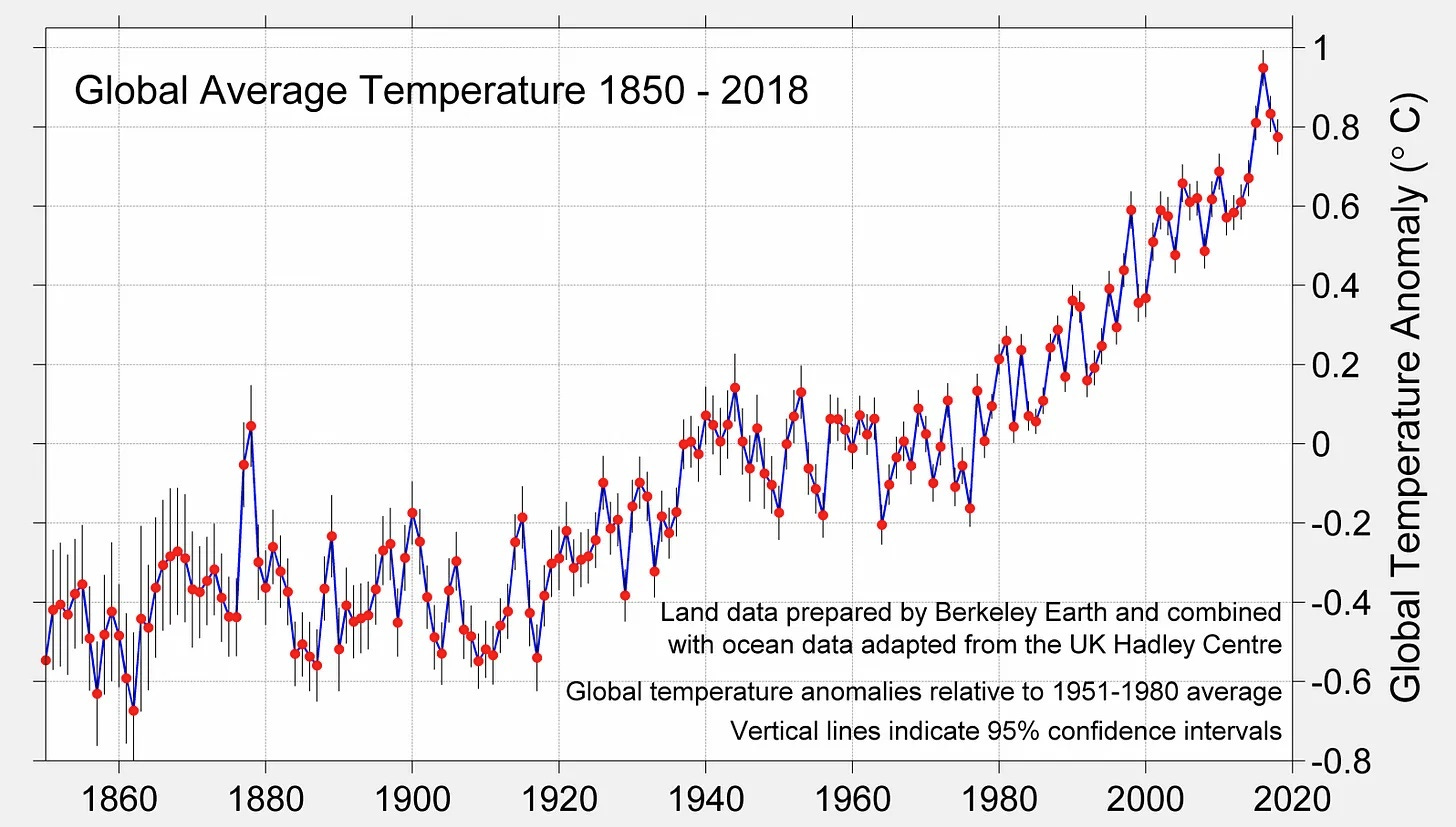
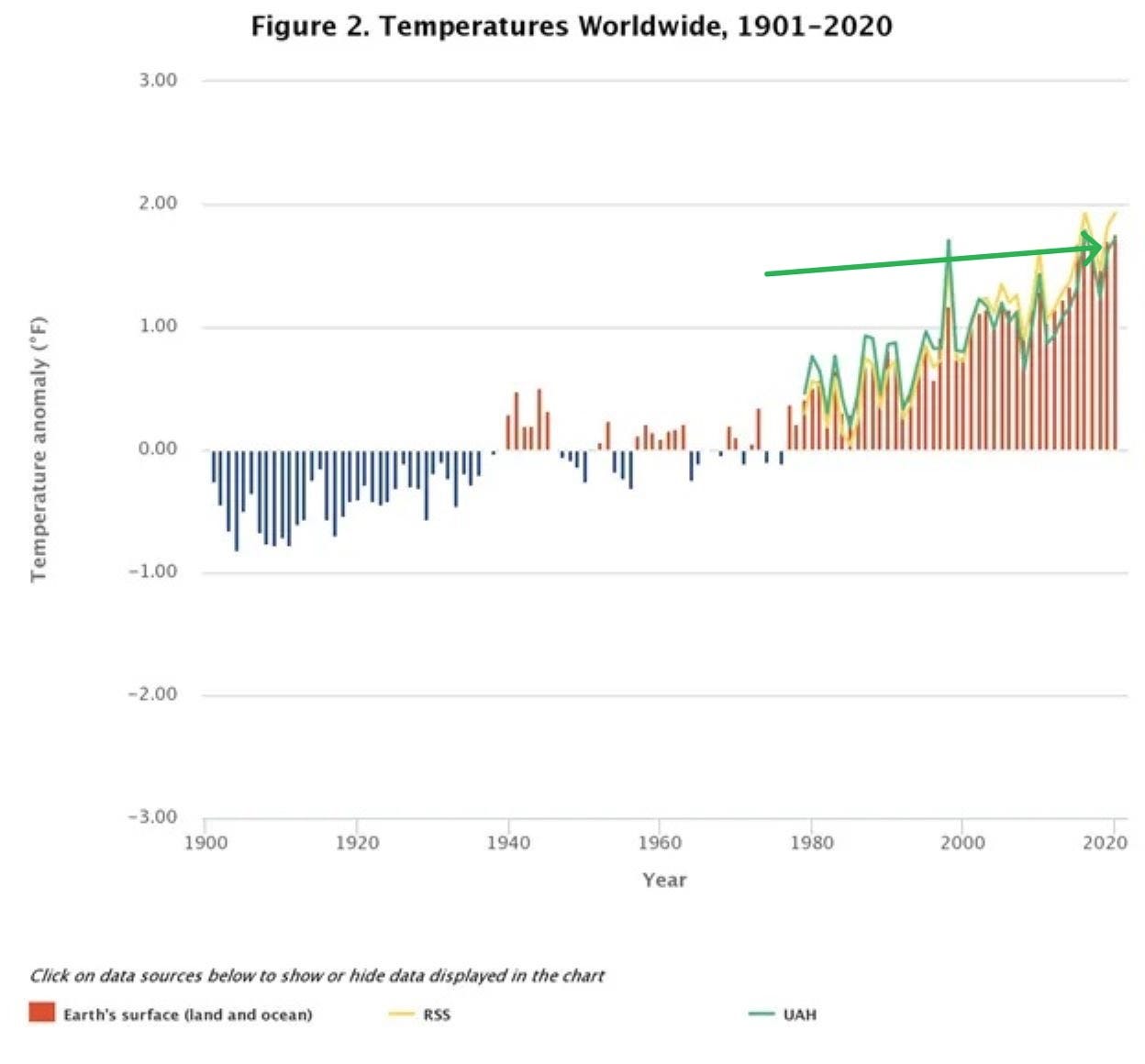
Remember, burning coal and oil does two things: it increases the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere which increases the global temperature, and it injects particulate into the atmosphere which lowers the global temperature. The resulting 0.07C per decade AVERAGE increase in the Global Mean Temperature between 1850 and 1980 reflected the balance between these two opposing forces. However, there is a crucial difference between these two pollutants.
The CO2 gas we put into the atmosphere is very long lived. Although most of its effect will be felt in the first 50–100 years it’s put into the atmosphere, it will continue to cause warming for around 10,000 years.
Anthropogenic aerosols on the other hand are very short lived. If you stop polluting and “clean up the air” they wash out of the atmosphere in about 3–4 years. When they do, the cooling effect they provide stops.
Now let’s look at this graph from the EPA again:
Lets be clear about what it’s showing. It’s a “Heat Wave Index” not a temperature record. On the EPA site it informs us that:
“Longer-term records show that heat waves in the 1930s remain the most severe in recorded U.S. history (see Figure 3). The spike in Figure 3 reflects extreme, persistent heat waves in the Great Plains region during a period known as the “Dust Bowl.” Poor land use practices and many years of intense drought contributed to these heat waves by depleting soil moisture and reducing the moderating effects of evaporation”
What this graph shows is that there was a massive number of heat waves during the 30’s.
What this graph also shows, is what happens when the amount of anthropogenic aerosols in the atmosphere suddenly goes down and the cooling effect they provide vanishes.

What happened to the climate in the 30’s was not natural. It was a period of rapid warming caused by losing the cooling effect of human particulate pollution. As soon as war time production jump started the global economy and pollution levels shot up, equilibrium between the two opposing effects began to be restored.
This is our future “RIGHT NOW”.
Estimates indicate that aerosol pollution emitted by humans is offsetting about 0.7 degrees Celsius, or about 1.3 degrees Fahrenheit, of the warming due to greenhouse gas emissions. This translates to a 40-year delay in the effects of climate change. Without cooling caused by aerosol emissions, we would have achieved 2010-level global mean temperatures in 1970.”
Climate effects of aerosols reduce economic inequality. Nature Climate Change, 2020; DOI: 10.1038/s41558–020–0699-y
Because in 2020 we deliberately reduced the levels of SOx particulate in the atmosphere in order to reduce global deaths from air pollution by about 22 million a year. In 2020 there was a change in the diesel fuels used by the shipping industry. This was not a trivial change.
Because, the shipping industry is among the world’s largest emitters of sulfur behind the energy industry, with the sulfur dioxide (SOx) content in heavy fuel oil up to 3,500 times higher than the latest European diesel standards for vehicles. Although energy production produces more SOx particulate overall, it has less effect on the Climate System.
Because power plants are fixed in one place and ships spread the SOx across the entire planet. “One large vessel in one day can emit more sulfur dioxide than all the new cars that come onto the world’s roads in a year.”
Cleaner Air in 2020: 0.5% sulfur cap for ships enters into force worldwide
From January 2020, the maximum sulphur content of marine fuels is reduced to 0.5% (down from 3.5%) globally — reducing air pollution and protecting health and the environment.
It’s been 3 years since that happened. The El Nino that’s starting is going to be turbocharged by a massive decrease in S0x (Sulfur Dioxide) levels in the atmosphere. They are falling rapidly.
We are in a “Geoengineering Trap”.
The reality is, that we have been geoengineering the atmosphere for about 150 years now. That has been masking the effects of our CO2 emissions.
If we cut back on our pollution and emissions, we won’t cool the planet, we will heat it up more in the short term. What the EPA “Heat Wave Index” graph is really showing, is what will happen when we do that.
We are in a trap and at some point in this century we are going to have to take the hit of an additional 1C of extremely rapid warming. We are now at roughly 1.2C of warming over the modern 1980 baseline only because of the unintentional geoengineering experiment that we have been engaged in. It is, in a sense, an “accounting trick” that has deferred a degree of warming until some unspecified date in the future.
It appears (based on the policy options they support) that the IPCC hoped to defer the bulk of that warming until after 2050. This makes a great deal of sense. Based on the current global political\economic reality there is very little possibility that we will achieve a global Net Zero economy by 2050. The Developed Nations aren’t going to finance or help the Developing Nations decarbonize their economies in the next few decades.
While CO2 levels will keep going up, there is an expectation that “new technologies” will emerge that will allow us to draw down the level of CO2 from the atmosphere in the decades between 2050 and 2100. Indeed, most of the projections for keeping Global Warming at or below 2C involve the use of CO2 sequestration technology that doesn’t exist yet.
We are betting that sometime in the near future we will find a way to remove massive amounts of CO2 cheaply and easily from the air and “sequester” or lock it away forever. Theoretically if we have this technology by 2050, we will be able to build the infrastructure necessary to accomplish this and balance the warming caused from reducing the particulate levels in the atmosphere with decreases in warming resulting from decreased CO2 levels.
We are trying to finesse Climate Change so that we don’t have a repeat of the 30’s and global temperatures don’t suddenly shoot up past 3C around 2050.
No matter what though, we are going to hit 2C of warming by 2050. It’s going to get a lot hotter over the next 30 years.
Of that, you can be certain.
It’s going to get HOT this year.
After 2022’s devastating heat waves and wildfires, scientists warn of even hotter year Jan 2023
Mercury soared above 40C across many parts of Europe in 2022, leading to many deadly wildfires and heat-related deaths.
UN’s weather agency: 2022 was nasty, deadly, costly and hot — April 2023
Killer floods, droughts and heat waves hit around the world, costing many billions of dollars. Global ocean heat and acidity levels hit record highs and Antarctic sea ice and European Alps glaciers reached record low amounts, according to the United Nations’ climate agency’s State of Global Climate 2022 report released Friday.
El Niño is coming, and ocean temps are already at record highs — that can spell disaster for fish and corals -April 2023
It’s coming. Winds are weakening along the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Heat is building beneath the ocean surface. By July, most forecast models agree that the climate system’s biggest player — El Niño — will return for the first time in nearly four years.
World could face record temperatures in 2023 as El Nino returns — April 2023
“Climate models suggest that after three years of the La Nina weather pattern in the Pacific Ocean, which generally lowers global temperatures slightly, the world will experience a return to El Nino, the warmer counterpart, later this year.
El Nino is normally associated with record breaking temperatures at the global level. Whether this will happen in 2023 or 2024 is not yet known, but it is, I think, more likely than not,”
- Carlo Buontempo, director of the EU’s Copernicus Climate Change Service.
With the heat, will come HEATWAVES.
‘Record smashing’ heatwaves: Research reveals which countries are most at risk.
Global research reveals countries where record-breaking heatwaves are likely to cause most harm - SciDaily April 25, 2023
Scientists used climate data and modelling to pinpoint where in the world temperature records are most likely to be broken and the communities in the greatest danger from extreme heat.
They found that “statistically implausible extremes” occurred in 31 per cent of the regions they analyzed between 1959 and 2021.
There was no particular pattern to where these temperature abnormalities were happening. This means these extremes, where current records are broken by margins that seem impossible until they occur, could happen anywhere.
“In this study, we show that such record-smashing events could occur anywhere. “We have seen some of the most unexpected heatwaves around the world lead to heat-related deaths in the tens of thousands.”
Dann Mitchell - study co-author Professor in Atmospheric Sciences at the University of Bristol Cabot Institute for the Environment.
A LOT of people are going to die from heat in the next few years.
Meanwhile.
India braces for heatwave amid soaring temperatures. What could it mean for Europe's food supplies?
End of Part Three
This is my analysis.
This is what I see.
This is my “Crisis Report”
-rc 05022023








So you would advocate for a project to spray aerosols in the upper atmosphere in the very short term?